

7 Support
Resources
Competence
Communication
Resources
Resources within
Jemison Metals are allocated based upon the results of the quality
planning and CAPEX processes, which support the quality policy and objectives.
Maintenance of equipment is conducted. These work instructions are
documented and scheduled based on manufacturers’ recommendations and/or JM’s
technical knowledge and experience.
Maintenance activities are performed by qualified personnel.
Assignment of personnel
within Jemison Metals is done on the basis of training, skills, and
experience.
The company has established resources for use of
a multi-disciplinary approach for developing facilities, processes and equipment
plans, including supporting services such as transport, communications, or
information systems. The layout of
the facilities minimizes the travel of material, facilitates synchronous
material flow, and maximizes the use of value-added floor space. Methods are developed for the
evaluation of the effectiveness of existing operations considering overall work
plan, appropriate automation, ergonomics and human factors, operator
productivity, storage and inventory levels.
A multi-disciplinary approach is used for
developing facilities, processes and equipment plans. Plant layouts are reviewed to
encourage efficient use of space, material flow and handling.
All instruments used to measure
mechanical/physical or dimensional features of purchased material,
customer-furnished material or completed product, and processing parameters must
be suitable and accurate to assure credibility of each feature measured.
The Maintenance Department or Head of Quality
is responsible for identifying the type of instrument capable of performing the
required measurement. Accuracy of
each instrument used for final acceptance must be calibrated as required by the
instrument manufacturer or by the instrument history.
Calibration standards are traceable to the
National Institute of Standards & Technology.
The standards used to verify accuracy must be more sensitive than the
instruments being calibrated.
Instruments used for final acceptance features
shall be capable of measurements tighter than the specified tolerance and shall
be used in a manner that ensures that measurement uncertainty is known and is
consistent with the required measurement capability.
Where test software or comparative references are
used, they are checked at prescribed frequencies to ensure they are capable of
verifying the acceptability of product.
When specified by contract, technical data
pertaining to measurement equipment is made available to the customer for
verification that the measurement equipment is functionally adequate.
Instruments found incapable of sustained accuracy
will require shorter calibration periods.
An instrument will be withdrawn from use if it is determined to be
unstable.
The Head of Quality is responsible for
determining the measurements to be made and for identifying the type of
instrument capable of performing the required measurement.
All inspection, measuring and test equipment,
which can affect product quality, is identified in calibration tracking software and calibrated at prescribed intervals against standards,
which are traceable to the National Institute of Standards & Technology (where
no such standards exist, the basis used for calibration is documented in the
calibration software and/or work instruction). The
calibration software details the equipment type, unique identification number,
location, and calibration interval.
The Calibration Software details the check methods, acceptance criteria and
actions to be taken when results are unsatisfactory.
All equipment used for acceptance measurements
are serialized and a certification decal attached, where practical. A calibration record is prepared and
maintained for each such instrument.
The record reflects in-service dates, calibration method and frequency. Accuracy of each instrument used for
final acceptance must be calibrated, as required, by the instrument manufacturer
or by the instrument history.
Suitable environmental
conditions are used for calibrations, inspections, measurements and tests being
carried out.
Inspection, measuring
and test equipment is handled and stored as to maintain accuracy and fitness for
use. Calibrated equipment and calibration standards are safeguarded to prevent
adjustments, which would invalidate the calibration settings.
Data is maintained for calibration control, inspection, measuring and test equipment records IAW QMP 7.5.
Material considered
suspect due to instrument malfunction or calibration integrity is investigated
so as to identify material accepted with the affected instrument. If a determination is made that a
customer may have received suspect material, JM immediately contacts the
customer to determine appropriate measures.
All measuring and test
equipment used to calibrate/test customer products or processing are calibrated
and maintained. Responsibility for
maintaining the calibration system, including records containing as-found
readings and instrument condition, is assigned to the Maintenance Department or
Quality Representative.
Organizational knowledge has many sources at Jemison Metals. Sources include; Individual Experience, External Standards (i.e. ASTM etc), Customer Needs, Technical Expertise, Customer Volume Useage. Organizational is stored with individuals, in proprietary software, and electronically. Organizational knowledge is maintained and made available to the extent necessary either through individual communication or via Jemison's Information Technology systems. When required, Jemison will seek out additional knowledge either through hiring, collaboration or purchase.
Competence, Awareness
Assignment of personnel
within Jemison Metals is performed on the basis of training, skills, and
experience.
We believe we have the
responsibility to continually improve our operation. The improvement of our
processes and thereby our products can only be effectively achieved by
implementing programs to improve the skills and capabilities of our employees. We will ensure that all employees
have the basic skills and understanding of technology necessary to meet the
requirements of their job, consistent with their responsibilities to the
organization.
We further believe that
the training and education process must change and improve on an on-going basis
to meet the challenging conditions of our environment.
The objectives of the program are to ensure that:
Ø
All
employees understand the organization and their role in it.
Ø
All
employees understand our processes.
Ø
All
employees have the basic skills to do their job and function effectively with
the organization.
Ø
All
employees have a sufficient understanding of current and any new technology
associated with their job.
Ø
All
employees understand the relevant need of our customers, our Quality Policy, and
our quality objectives.
Ø
All
employees have the necessary skills to effectively participate in continuous
process improvement programs.
Ø
Employees understand the relevance and importance of their activities.
Employee Training
The foundation of the Jemison Metals
quality program is superior workmanship.
Establishing standards and the subsequent training of our people has been
the key to growth. Customer
satisfaction is a testimonial to the effectiveness of our training program.
The company identifies
the training needs of all personnel performing activities affecting quality, and
provides the required training.
Personnel performing specific tasks are qualified on the basis of appropriate
training, and/or experience, as required.
Performance and Training Records
All employees are
assessed by their supervisors and managers to determine if their qualifications
are adequate or if they need to be supplemented by additional training.
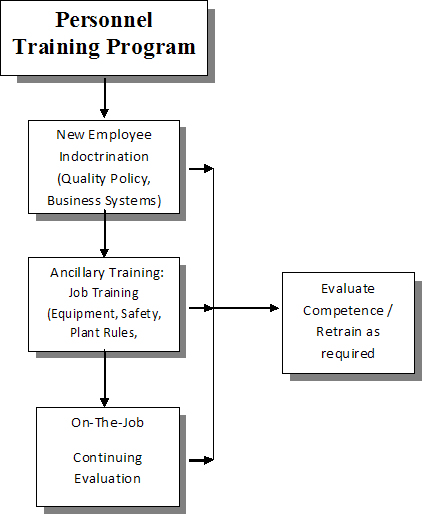
The employee training
is composed of three phases. The
initial or preliminary phase is a formal indoctrination of company QMS, goals,
and business systems (much of which is documented electronically by HR Software). The second
phase is introduction to proper use of equipment.
The third phase is on-the-job training, which includes job specific
ancillary training.
Jemison Metals
maintains records of experience, education, skills, and internal and external
training provided to employees.
Reviews conducted by the employee’s supervisor are used to evaluate the
effectiveness of training and identifies when additional ancillary training may
be required.
Awareness
All employees are trained on the quality policy, what it means relative to their role in the organization, and their relevant quality objectives during the initial hire process. Additionally, it is explained to employees how their work contributes to the effectiveness of the QMS and how nonconforming work can be counterproductive to the QMS.
Communication
Communication within JM is critical to maintaining an effective Quality Management System. Communication between the various levels and functions starts with the Management Review Meetings. At these meetings all aspects of the Quality Management System are discussed with the Top Management Group. The Internal Auditing and Corrective/Preventive Action system are used to collect the information needed to evaluate the effectiveness of the Quality Management System. The Quality Objectives and performance measures are used to track progress and to identify opportunities for improvement. Customer and internal communication is communicated to warehouse personnel to ensure key metrics, customer complaints, and customer returns are disseminated. The frequency of communication, at a minimum, is as follows: Management Review - Annual; Key Metrics - Monthly, Customer Complaints - Monthly, Customer Returns - Monthly. The head of quality has responsibility to disseminate the information to the rest of the organization. Operations Management and/or Local QA disseminates relevant metrics and information to warehouse employees.
Personnel Training
Program Flowchart
Documented Information
This manual contains
references to the Quality Manual Procedures/Process Maps that describe the
processes required to implement the Quality Management System at Jemison
Metals in compliance with the requirements of ISO 9001.
The Quality Management
Procedures, in turn, make reference to other related procedures, work
instructions and flowcharts necessary to describe the sequence and interactive
nature of the processes to ensure conformity to customer specifications and
requirements.
Document Hierarchy
Document Creating and Updating
Documents in the JM Quality Management System that are pertinent to product quality are identified and controlled. All documents and data are reviewed and approved for adequacy by authorized personnel.
“Controlled Documents”
include any means of conveying technical and procedural information wherein the
intended user must be assured of having electronic access to the current
approved version of that information. A master list of controlled documents is
maintained that specifies the latest revision and effective date. Controlled
documents are distributed electronically. Printed versions used for reference,
unless in Controlled Manuals, are considered “Uncontrolled”.
Appropriate documents
are available at locations where operations essential to the effective
functioning of the Quality Management System are performed.
Quality Policy Manual
The Corporate Quality Policy Manual has been prepared to inform employees and customers of the management policies and objectives for the quality of its products and services. The manual is the guide to our quality functions, which are designed to ensure that Jemison Metalss products meet or exceed our customers’ requirements, and the requirements of ISO 9001.
Quality Management Procedures and Process Maps
Work Instructions
These documents address
the “how to” elements of our process
which define in detail those activities controlling or impacting product
quality.
For those applications
that require expanded, detailed, how-to instructions, facility routings and
On-The-Job training provide those details.
These instructions are controlled documents and
are available at the operations they define to ensure conformance with
specifications. Modifications to the
instructions are made whenever changes occur to customer and/or Jemison
Metals standards.
External Documents
JM maintains current
versions of all documents that originate outside of the company that have an
impact on quality. These include but
are not limited to customer, manufacturer, and industry specifications, prints and
standards. External documents that
define customer requirements are obtained or verified as current before an order
is accepted. Electronic customer part specs are stored in BEST & Invex.
JM promptly reviews
all changes to external documents. When these changes necessitate
a change to internal controlled documents, the changes are made and a record is
maintained of those changes.
Document Changes
Document changes are reviewed and authorized by the same authority that issued the original document unless the revised document specifically states otherwise. Revised portions of documents are distributed with a Document Change Request/Notice, and obsolete documents are promptly replaced and identified to ensure against unintended use. Obsolete documents that need to be retained for legal and/or knowledge preservation are appropriately identified.

Record Collection
A control system is maintained for the identification, storage, protection, retention, indexing, access, filing, maintenance and disposition of quality records. Records may be in the form of any type of media, such as hard copy or electronic media.
Quality records are
retained to demonstrate conformance to the specified requirements of ISO 9001
and the effective operation of the Quality Management System. Records are generally collected and
stored by the department generating the record.
This ensures ease of retrieval and verification. Records are cataloged and filed to
facilitate retrieval. Pertinent
quality records from suppliers shall be an element of this data.
Applicable Records
Quality records are
retrievable and traceable to shipped product in order to verify compliance to
customer requirements. Where agreed
contractually, quality records are made available for evaluation by the customer
or the customer’s representative for an agreed period of time. Other quality records are accessible
for verifying the effective operation of the JM Quality Management System,
including but not limited to such areas as supplier quality records, internal
audits, corrective actions, supplier assessments, management reviews,
calibration, training, product review, inspection, testing and product
identification.
Retention, Responsibility and Disposition
The comprehensive listing of required records indicates the following:
Ø Storage location for each
quality record
Ø Retention time for
storage and disposition of each quality record (complies with specific
Ø Responsibility for control of
each stored quality record
Applicable Quality
Management Procedures and Documents:
Ø QMP 7.5 Documented Information
Ø MOP 1 Management Review
Ø SOP 1
Training
Ø SOP 3 Control of Monitoring and Measuring Resources
Revision History
| Date | Section | Description | Revision |
| 9/15/25 | External Docs | Reference to Stelplan updated. | B |
| 11/22/19 | Control Methodology | Updated to reflect GageTrak Calibration Software & Consideration of In-House Calibration Environment as well as reference to HR Software (i.e. Dayforce in Performance & Training Records 2nd Para.) | A |
| 7/20/18 | n/a | n/a | Original |